Introduction
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is one of the most resource-rich countries in the world. Located in Central Africa, the Congo possesses vast deposits of minerals, fertile land, dense forests, and abundant water resources. These natural assets give the country enormous economic potential and global importance. However, despite this wealth, the Congo continues to face significant development challenges. Understanding Congo’s resources helps explain both its global strategic value and its internal struggles.
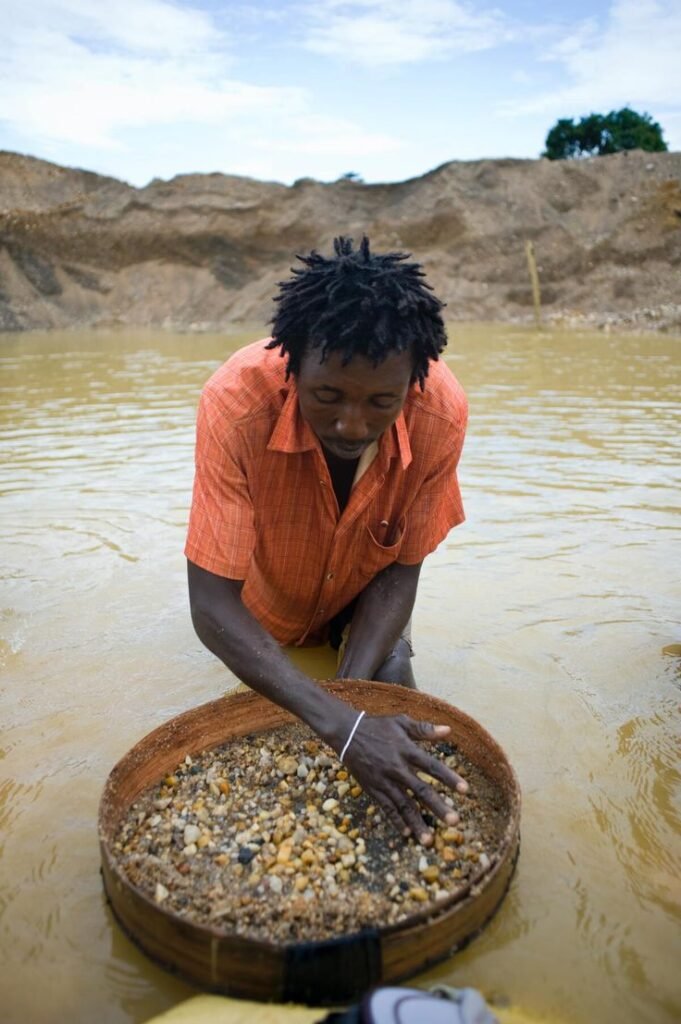

Overview of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic and Natural Setting
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is the second-largest country in Africa by land area. It lies along the equator and includes rainforests, savannas, rivers, and mineral-rich highlands. The Congo River, one of the world’s longest and deepest rivers, plays a central role in transportation, agriculture, and energy production.http://www.truthfrontier.com
Population and Economic Context
The country has a large and growing population and relies heavily on natural resources for economic activity. Mining and agriculture dominate the economy, while manufacturing and infrastructure remain underdeveloped compared to the country’s potential.http://www.bbcnews.com
Major Mineral Resources of Congo
Copper Resources
The Congo is one of the world’s leading producers of copper, especially in the Katanga region. Copper is essential for electrical wiring, construction, renewable energy systems, and electronic devices. Congo’s copper reserves play a crucial role in the global supply chain, particularly as demand for clean energy technologies increases.
Cobalt: A Strategic Global Resource
Congo is the largest producer of cobalt in the world, supplying a major share of global demand. Cobalt is a critical component in lithium-ion batteries, which are used in electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops, and energy storage systems. This makes Congo extremely important to the global transition toward clean energy and electric mobility.
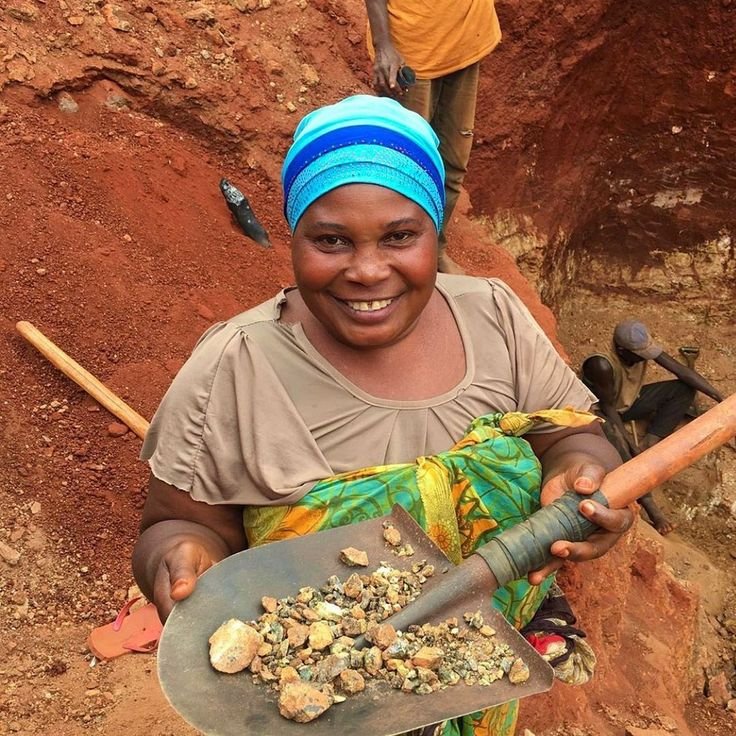

Gold Deposits
Gold is another valuable resource found in several regions of the Congo, particularly in eastern provinces. Gold mining provides income for local communities but has also been linked to illegal mining and conflict financing when not properly regulated.
Diamonds
Congo has significant diamond reserves, both industrial and gem-quality. Diamonds are used in jewelry as well as in industrial cutting and drilling tools. For many years, diamonds were one of Congo’s major export resources.
Coltan and Rare Minerals
Importance of Coltan
Coltan, short for columbite-tantalite, is a vital mineral used in electronic devices such as mobile phones and computers. The Congo holds a large portion of the world’s coltan reserves, making it strategically important in the global technology industry.
Other Rare Minerals
In addition to coltan, the Congo has deposits of tin, tungsten, lithium, and uranium. These minerals are increasingly valuable due to their role in advanced technologies, renewable energy, and defense industries.
Forest Resources of Congo
Congo Basin Rainforest
The Congo Basin rainforest is the second-largest tropical rainforest in the world after the Amazon. It covers a significant portion of the country and is a major global carbon sink, helping regulate the Earth’s climate.
Timber and Biodiversity
Congo’s forests provide valuable timber resources such as mahogany and teak. They are also home to extraordinary biodiversity, including endangered species like gorillas, okapis, and forest elephants. Sustainable forest management is essential to protect these ecosystems.
Water Resources and Hydropower
Congo River System
The Congo River is one of Africa’s most important water resources. It supports fishing, transportation, agriculture, and daily livelihoods for millions of people. The river basin provides fertile soil and irrigation potential across the country.
Hydroelectric Power Potential
The Congo has one of the world’s greatest untapped hydropower potentials. Projects like the Inga Dams could supply electricity not only to the Congo but also to neighboring countries. Reliable energy could transform industrial growth and improve living standards.

Agricultural Resources
Fertile Land and Crop Production
Congo has vast areas of fertile land suitable for agriculture. Major crops include cassava, maize, rice, bananas, coffee, cocoa, and palm oil. Agriculture supports a large portion of the population and plays a key role in food security.
Livestock and Fisheries
In addition to crops, the Congo has resources for livestock farming and freshwater fisheries. Rivers and lakes provide fish that serve as a major source of protein for local communities.
Economic Importance of Congo’s Resources
Contribution to National Economy
Natural resources are the backbone of Congo’s economy, contributing significantly to exports and government revenue. Mining, in particular, accounts for a large share of foreign exchange earnings.
Role in Global Markets
Congo’s minerals are essential to global industries, especially electronics, renewable energy, and electric vehicles. The country’s resources directly influence global supply chains and international economic strategies.
Challenges in Resource Management
Conflict and Resource Exploitation
For decades, competition over resources has fueled conflict in parts of the Congo. Illegal mining, armed groups, and smuggling have undermined stability and diverted wealth away from public development.
Environmental Impact
Unregulated mining and deforestation have caused environmental damage, including soil erosion, water pollution, and loss of wildlife habitats. Balancing economic growth with environmental protection remains a major challenge.
Governance and Transparency Issues
Weak governance, corruption, and lack of infrastructure have limited the benefits of resource wealth for ordinary citizens. Improving transparency and regulation is essential for sustainable development.
International Efforts and Sustainable Development
Responsible Mining Initiatives
International organizations and governments are promoting responsible sourcing of minerals from the Congo. Certification systems and ethical supply chains aim to reduce conflict financing and protect human rights.
Environmental Conservation Programs
Efforts to protect the Congo Basin rainforest include conservation projects, climate finance programs, and community-based forest management. These initiatives recognize the global importance of Congo’s ecosystems.
Future Potential of Congo’s Resources
Opportunities for Economic Growth
With proper management, Congo’s resources could drive industrialization, job creation, and poverty reduction. Investment in infrastructure, education, and energy could unlock long-term growth.
Importance of Sustainable Resource Use
Sustainable development is key to ensuring that Congo’s natural wealth benefits future generations. Responsible mining, environmental protection, and fair distribution of resource revenues are essential goals.
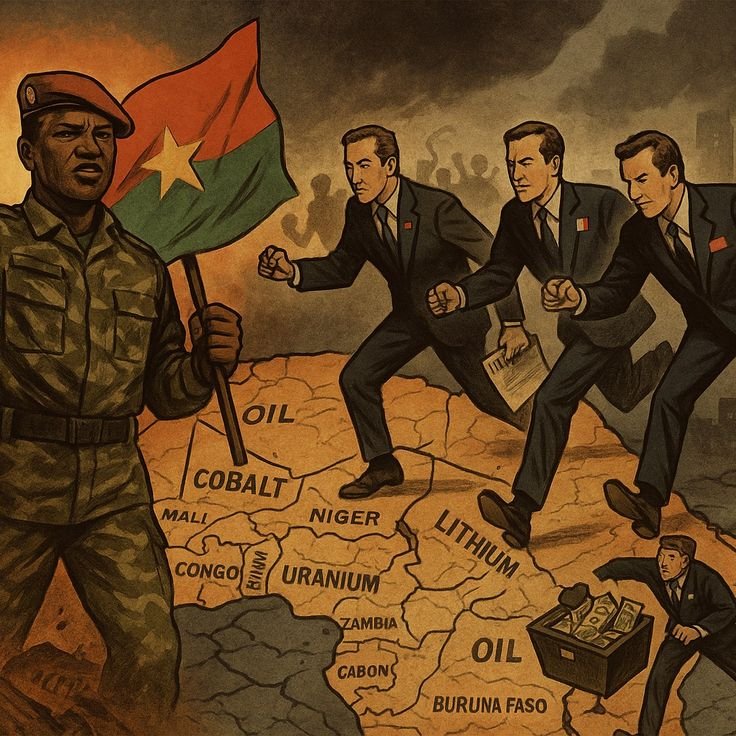

Conclusion
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is one of the most naturally gifted countries on Earth, endowed with vast mineral reserves, rich forests, powerful rivers, and fertile land. These resources give it immense national and global importance, especially in an era of technological and energy transition. However, the true value of Congo’s resources lies not only in extraction but in responsible management, peace, and sustainable development. With stability, transparency, and global cooperation, Congo’s natural wealth has the potential to transform both the nation and the world.